May 24, 2013
What is Bitcoin
- A math-based currency without a central bank
- Based on P2P techniques, totally decentralized
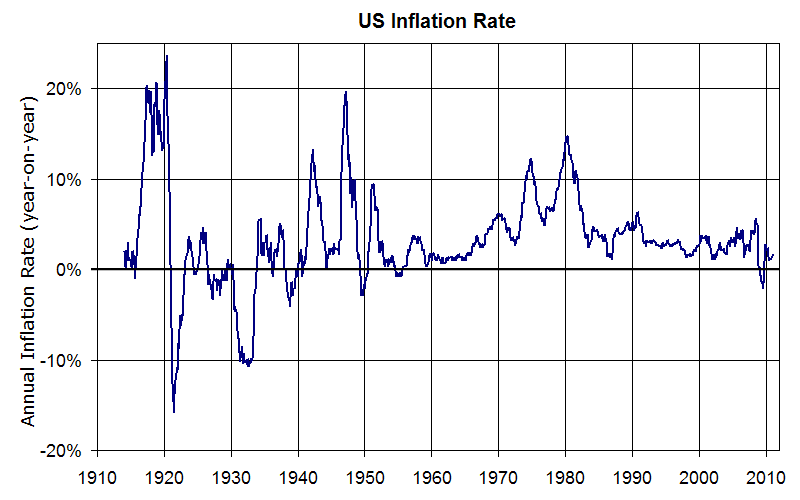
- No inflation
- Infinitely divisible
- Born in 2009, created by Satoshi Nakamoto (中本 聰)
Why do we need Bitcoin
- Credit money is not reliable
- Governments are creating huge inflations to repay their debts
- Everything is tracked and controlled by the authoritiy
Must money issued by the government?
- In the USA from 1837 to 1866, anyone can issue paper money
- BerkShares: a local currency issued for the Berkshire region of Massachusetts by the BerkShares company.
- Hayek: Denationalization of Money
How is Bitcoin issued without a central bank
- Gold does not have to be issued by an issuer, only be dug by miners
- Everyone can claim he found a Bitcoin as long as others accept
- The problem is: why do I accept money you created?
What is the value of Bitcoin
-
As a general equivalent, like gold, it is:
- Easy to distinguish and measure
- Hard to generate
- Limited in a certain amount
- Storable
- Dividable
- Tradable
- It has no difference with other commodity: the price is decided by the supply and the demand
-
According to Mises Regression Theorem:
- Today's value depends on yesterday's value
- Till the first day it has value
How is Bitcoin running
-
How does a decentralized monetary system record the owner of every coin?
- It is simple and brutal: Every node in P2P network stores all transactions from the first day of Bitcoin's birth
- Thus you can calculate out how much everyone has
-
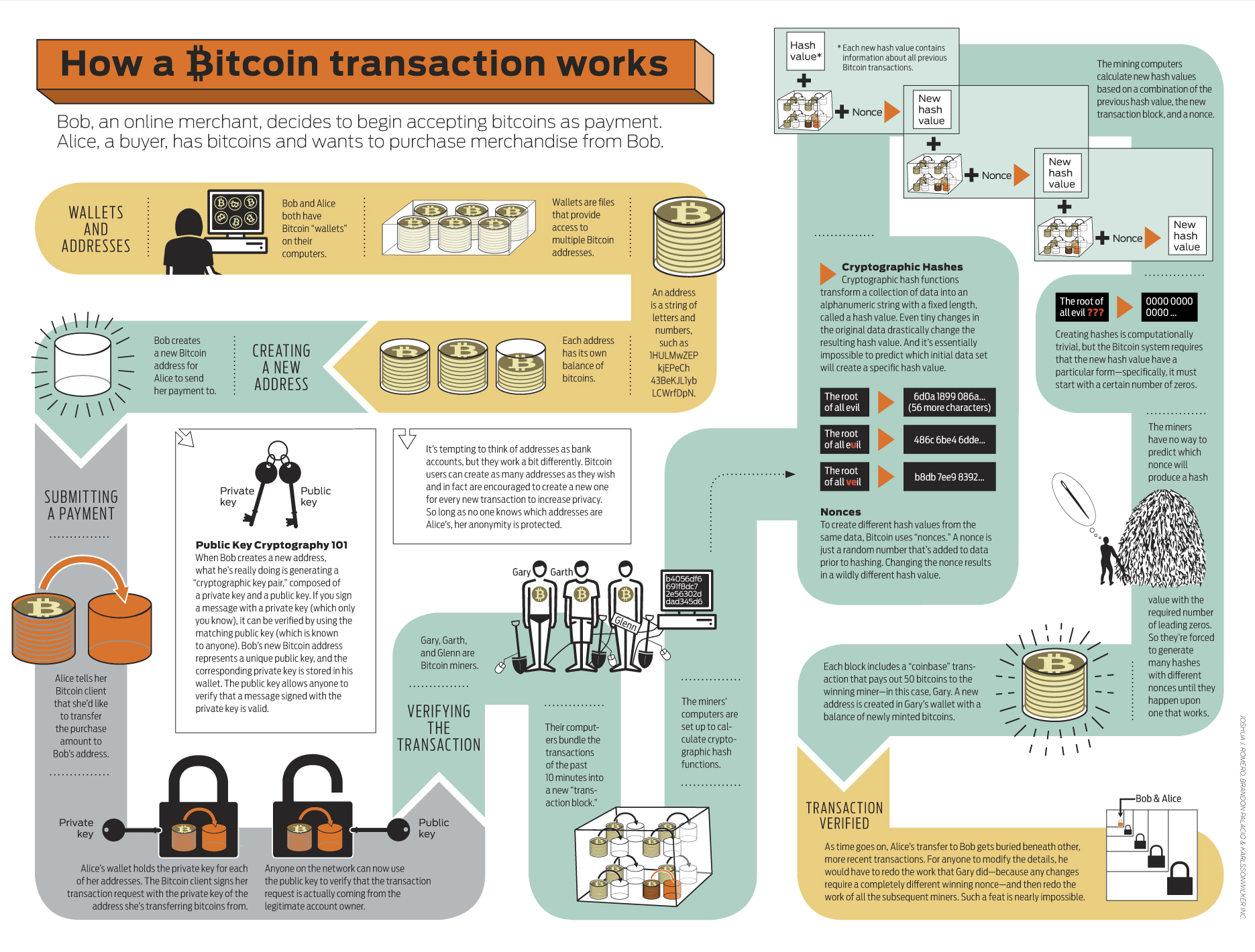
How is the ownership of a Bitcoin transfered?
- An account is a pair of private key and public key.
- The public key is your address or accounts number.
- The private key proves your ownership,
- If Alice pays a certain amount of money to Bob, Alice should sign a message with her private key, which contains the last hash, Bob's public key and the amount of money she is going to transfer.
- There should be some guarantors that witness this transaction.
- Bob will not acknowledge this transaction until he knows this transaction indirectly from some other people.
How is Bitcoin running
-
How are transactions recorded?
- We need a unique history of transactions, called blockchain.
- Blockchain is a chain of blocks. Every block contains some transactions with hashed signatures, and linked to the previous block.
- The work of generating new blocks is called mining, which is the process of packaging transactions into a block.
-
How to sign a transaction?
- It relys on a mechanism called "Proof of work" (Hashcash Algorithm).
- You can add anything into a message (to be signed), as loog as the hash code of it meets some requirements.
- For example, the hash code is leading with a number of 0.
- It is proved that the best approach of solving this problem is exhaustive enumeration.
How is Bitcoin running
-
Who are creating blocks?
- Since creating new blocks costs a lot, there must be incentives.
- The solution is, the one who created a block will get some Bitcoin as reward: this is how Bitcoin created.
- Miners can also get trading fees spend by traders.
- Only the longest blockchain will be accepted.
-
How to set the difficulity and reward of mining?
- P2P network will tune the difficulity according to the computing power.
- The reward of mining every block is 50 at first and halves every 210000 blocks.
The workflow of Bitcoin
Mining
- Mining is essential for Bitcoin system, no mining no transaction.
- Since more and more people are mining, the reward is getting lower.
- CPU -> GPU -> FPGA -> ASIC
- Big mining pools
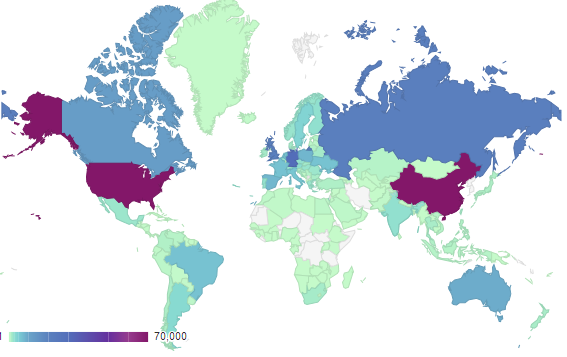
Nodes Distribution of Bitcoin Network
There are more nodes in China than USA
Economic features of Bitcoin
- Not freezable
- Very hard to track
- Trading cost is very low
- No Taxation
- In-born deflation
- Global market
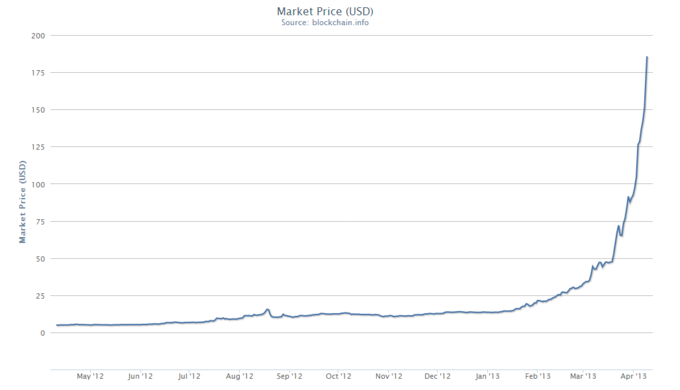
Market Price of Bitcoin
Criticisms
- Too many speculators
- Price fluctuation is too huge
- Hard to tax
- Anonymous trading
- Conducive to money laundering
- Arbitrage between markets is possible
- Attacts lots of system invaders
Scalability issues
- About $160 million costs in the last year (servers, electricity, labor), which means $11 per transaction!
- History of all transactions are too large: for now serveral Gigabytes.
- If it scales to as large as VISA, one block would be as large as 1GB.
P2P network's dilemma
- Protocol is not able to upgrade smoothly.
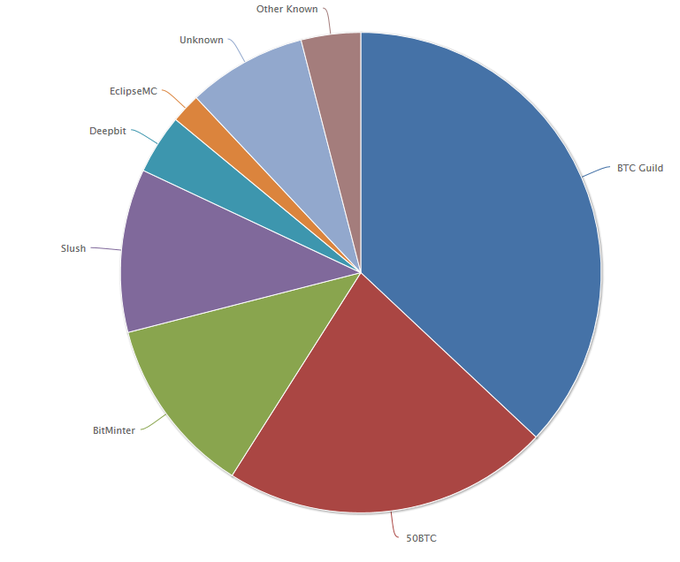
- Mining is more and more centralized, thus 51% attack is becoming possible.
Real World Bitcoin
- You can buy and sell Bitcoin from exchanges with credit money
- The biggest one is MtGox
- Blockchian.info provides an online wallet service.
- BitInstant devotes in changing Bitcoin with offline money and goods.
- BIPS exchanges different kinds of virtual money.





Any questions?
Thank You!
May 24 2013